Therapeutic Benefits of Nutrition for Diabetes
By Nmami Agarwal 19-Apr 2020 Reading Time: 4 Mins
Healthy diabetes eating plan includes a meal plan that helps you control your blood sugar levels. Having a well-balanced diet could be your saviour. Snacking healthily with adding variety is recommended and not over indulging in one particular food item.
Here are a few therapeutic benefits for diabetes:
- Know the Glycemic Index (GI) of your food
- Opt for complex carbs over simple carbs
- Ditch the sugar
- Fibre game strong
- MUFA and PUFA over saturated fats
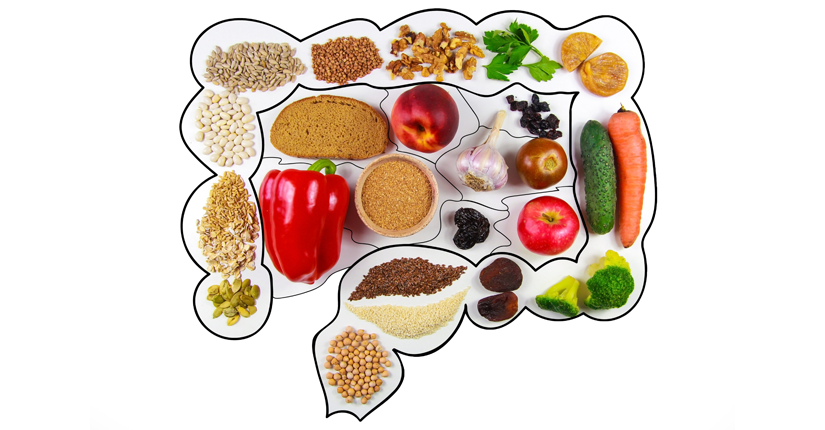
Diabetes should use the glycemic index to select foods, especially carbohydrates. This method ranks carbohydrate-containing foods based on their effect on blood glucose levels. Choose food items like roasted chanas, whole grains, broccoli, brown rice are all low in GI(GI=55).
Since carbohydrates break down into glucose, they have the greatest impact on your blood glucose level. To help control blood sugar levels, learn to calculate the amount of carbohydrates you are eating so that you can adjust the dose of insulin accordingly. Choose complex carbs options like brown rice over white rice, oats over wheat flour and more.
People with diabetes or those at risk (in prediabetic stage) are advised to avoid sugar-sweetened beverages (including fruit juices) in order to control glycemia and weight and reduce their risk for cardiovascular disease and fatty liver and should minimize the consumption of foods with added sugar that can be displaced with healthier, more nutrient-dense food choices.
Make sure to include a good source of fiber containing food with every meal or snack. Add some whole grains to the morning meal like oats. Use whole grain breads for lunch or snacks. Eat less potatoes. Instead, try brown rice or less well-known grains like ragi, jowar, in combination with wheat berries, or quinoa.
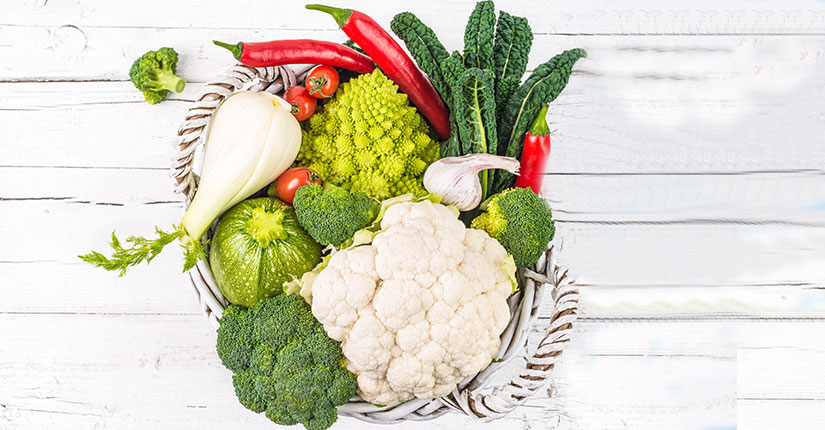
Include beans/legumes which are an excellent source of slowly digested carbohydrate as well as a great source of lean protein. Strive to include a variety of fresh fruits and vegetables in meals every day.
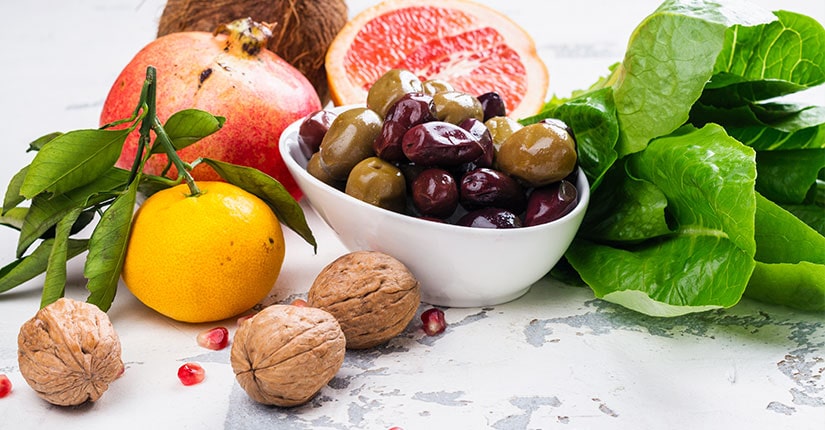
Foods high in Monounsaturated Fatty Acids (MUFA) include avocado, some fatty fish, and nuts. Diets rich in MUFA or Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids (PUFA) and lower in saturated fat are associated with a reduced risk of heart diseases. Replacement with PUFA is linked to improved glycemia, insulin resistance, and insulin secretion capacity.
In general, saturated fats are discouraged because they increase LDL (bad)cholesterol and total cholesterol concentrations. Diets high in saturated fats have been implicated in an increased risk of heart disease.
Over to you
Portion control and having small and frequent meals is the best way and should be followed. Managing your blood glucose levels could help you more in managing diabetes better. Consulting a dietitian and doctor is advisable.