Public Health Awareness Week: Obesity
By Nmami Life Editorial 05-Apr 2021 Reading Time: 4 Mins

The Obesity epidemic is the largest leading health problems that has been shifted from being a problem in rich countries, to one that spans all income levels. Globally, 8% of deaths in 2017 were the result of obesity- this represents an increase from 4.5% in 1990
Body mass index (BMI) is used to assess if a person is at an appropriate weight for their age, sex, and height. The measurement combines height and weight. A BMI greater that 30 suggests that a person may have obesity.
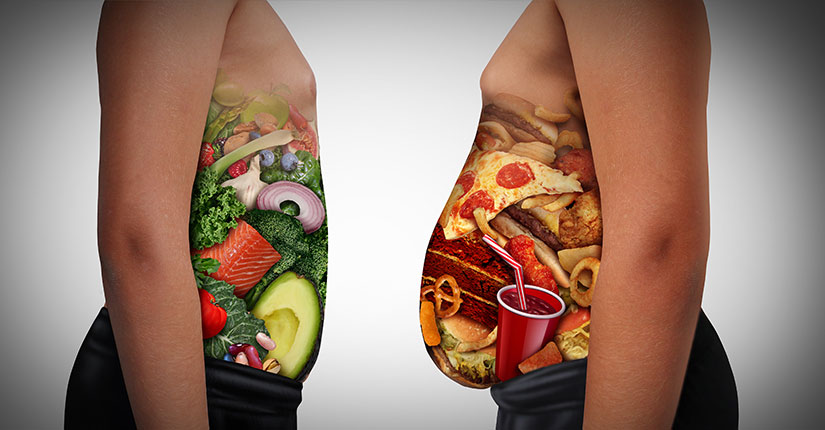
Obesity is a condition that leads to serious physical health in which a person has excess body fat. To be precise being more than just a number on a scale or the size of someone’s body, obesity can increase a person’s risk of diseases and health problems, including high blood pressure, diabetes and heart disease.
Causes of Obesity
Primary Cause:
- Consuming more calories, fat and sugar
- Sedentary Lifestyle without exercise
Secondary Cause:
- Genetics
- PCOS
- Hypothyroidism
- Prader- Willi Syndrome
- Cushing Syndrome
- Psychological Factors
- Medications
Health Risks
For most people, obesity becomes a lifelong struggle that is caused by multiple factors, and many underlying reasons that lead to obesity in an individual. The demand to manage obesity is clear as obesity increases your risk of many other diseases and health problems. Such as:
- Heart disease
- Diabetes
- High Blood Pressure
- Osteoarthritis
- Gallstones
- Depression
- Insomnia
- Dementia
- Sleep Apnea
Depression can be a common effect of obesity. Many obese people suffer emotional distress. Due to the target on physical appearance in our culture, which equates slimness with beauty, obese people may feel unattractive.
Obesity is also considered a major risk factor for the development of diabetes mellitus. People who were at a high risk of developing diabetes decreased their risk by almost 60% with less than 10% weight loss in three years.
Treating Obesity
The treatment should be designed to achieve and maintain a “healthier weight”, not necessarily an ideal weight. So, the only yet the best way to treat obesity is to eat a healthy, reduced-calorie diet and exercise regularly. To do this you should:
- Have a balanced, calorie-controlled diet as recommended by your health professional (such as a dietitian)
- Indulge in activities such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming 30-45mins, 4-5 times a week
- Be a slow eater and avoid situations where you know you could be tempted to overeat
Quick Obesity Facts:
- Obesity lowers the life’s duration by an average of 3 to 10 years, depending on how severe it is.
- Being obese and overweight contributes to at least 1 in every 13 deaths in the World.
- More than 60 chronic diseases are linked with Obesity.
Over to you:
There’s no “quick fix” for obesity. Regularly monitoring your weight, setting realistic goals and healthy eating combined with an active lifestyle is the best way to prevent obesity.